Procedures
- Blood, nerve water analysis and skin biopsy
- Electroencephalography (EEG)
- Electrocardiography (ECG)
- Magnetic resonance tomography (MRI)
- Neuropsychological assessment
- Positron Emissions Tomography (PET)
- Oculography - Recording of eye movements (eye tracking)
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
- Quantitative motor methods/actigraphy/ gait analysis
- Spiroergometry
- Ultrasound examination (sonography)
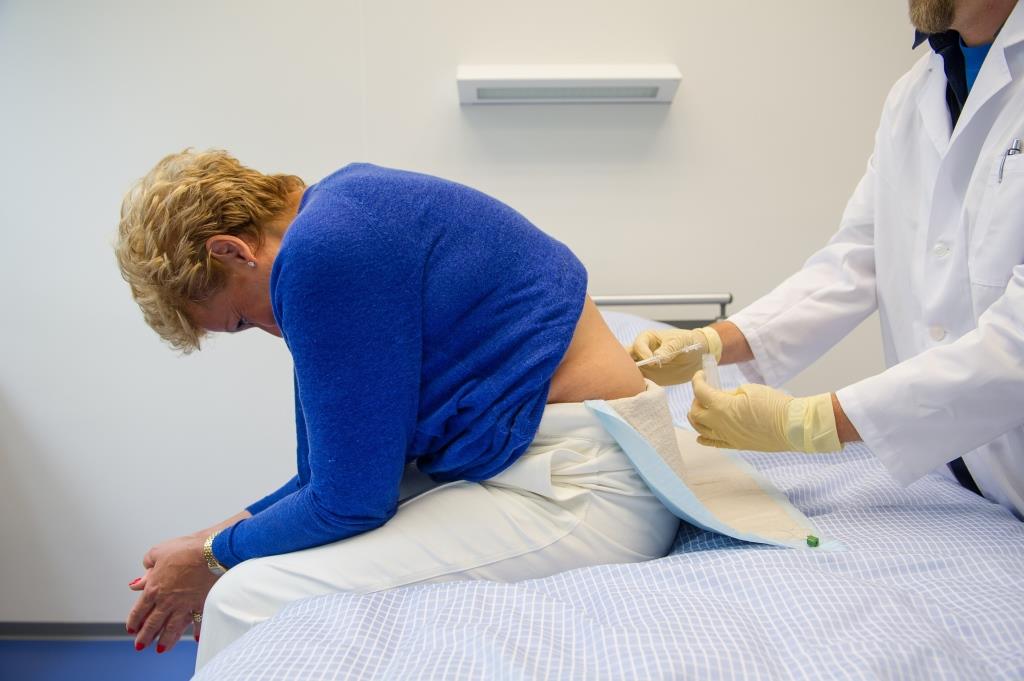
Blood, cerebrospinal fluid analysis and skin biopsy
Biomaterial is extracted, analyzed and stored to determine different risk markers for neurodegenerative diseases. Combining the results of biomaterial and clinical examinations should help to characterize neurodegenerative diseases in order to be able to detect diseases as early as possible and to classify them better.
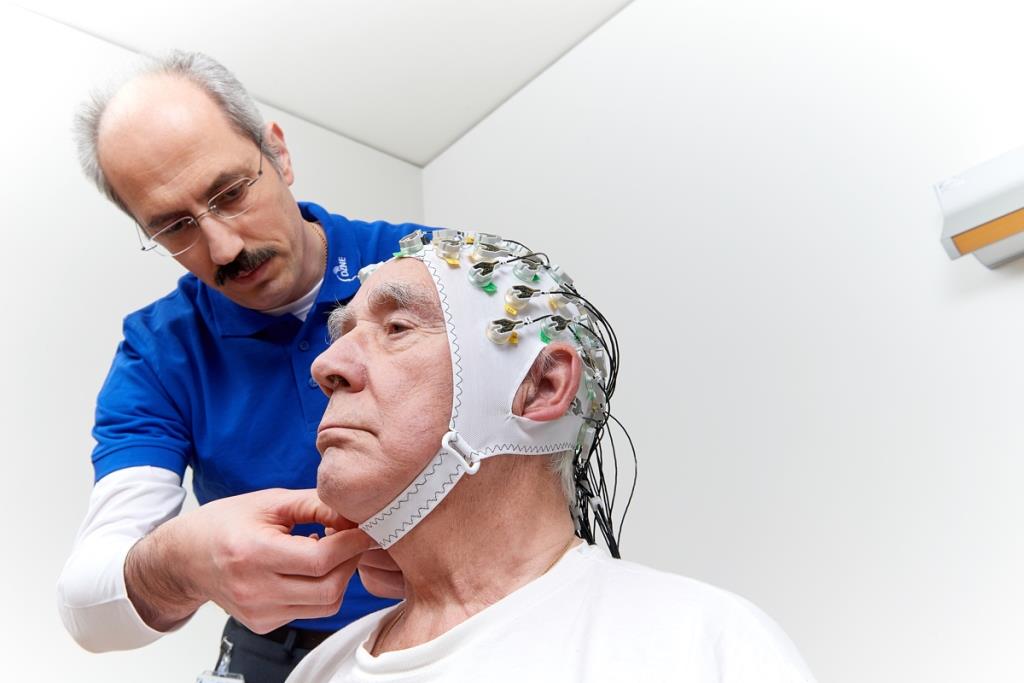
Electroencephalography (EEG)
Electroencephalography is used to record electrical signals that are generated naturally during brain activity by means of surface electrodes on the scalp with a high temporal resolution. The examination is safe, painless and can be repeated as often as required.
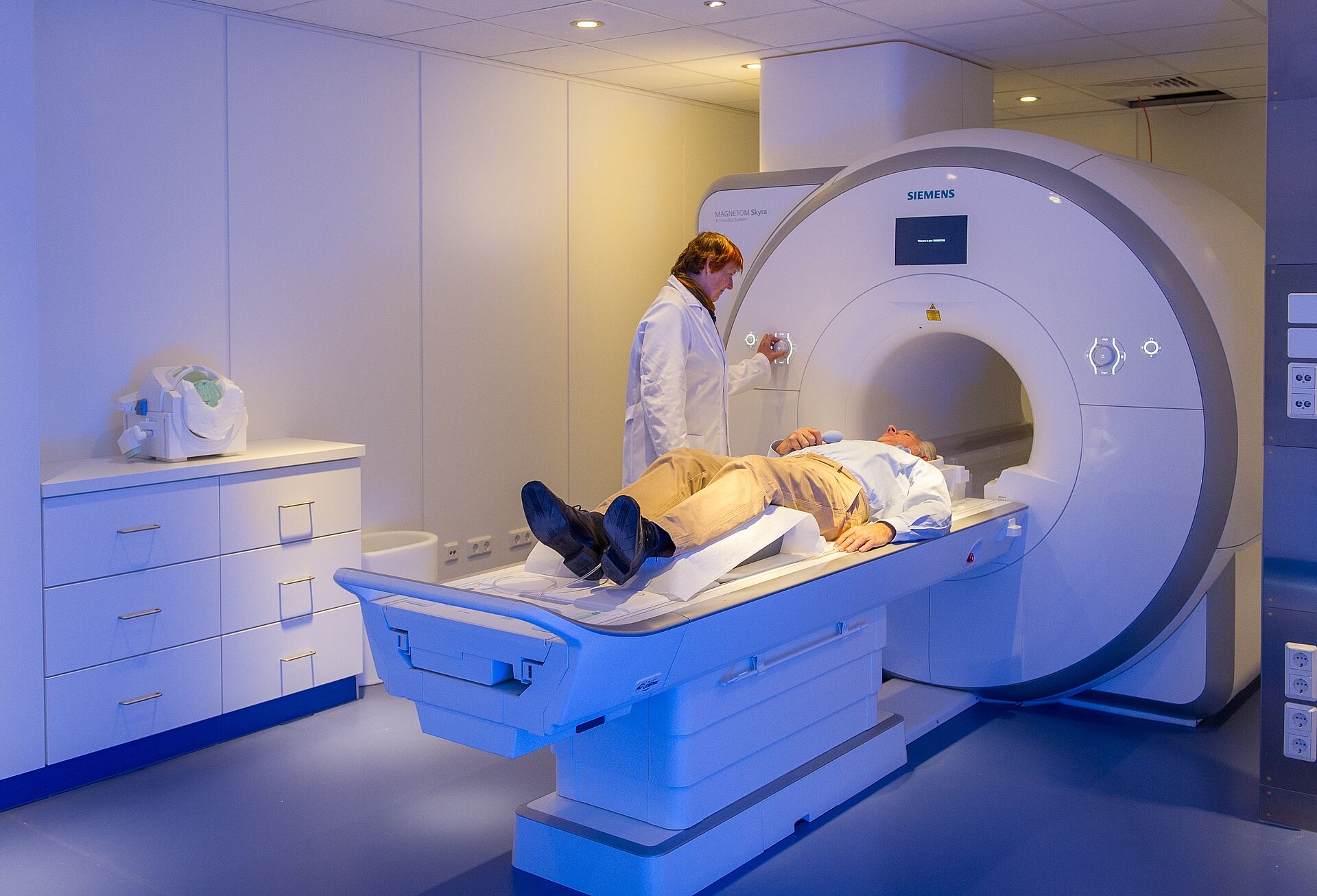
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI, also known as magnetic resonance tomography) enables high-resolution imaging of brain structures (structural MRI) and the display of changes in brain activation (functional MRI, fMRI) using magnetic fields. The MRI physics group of the DZNE operates two tomographs: a 3 Tesla (Siemens® Skyra) and a 7 Tesla tomograph (Siemens®), which are used in cooperation with the Center for Clinical Research. Tesla designates the magnetic field strength. While 3 Tesla is also used for medical diagnostic devices, 7 Tesla devices are currently only used for research purposes. There are only about 100 of these 7 Tesla devices worldwide.
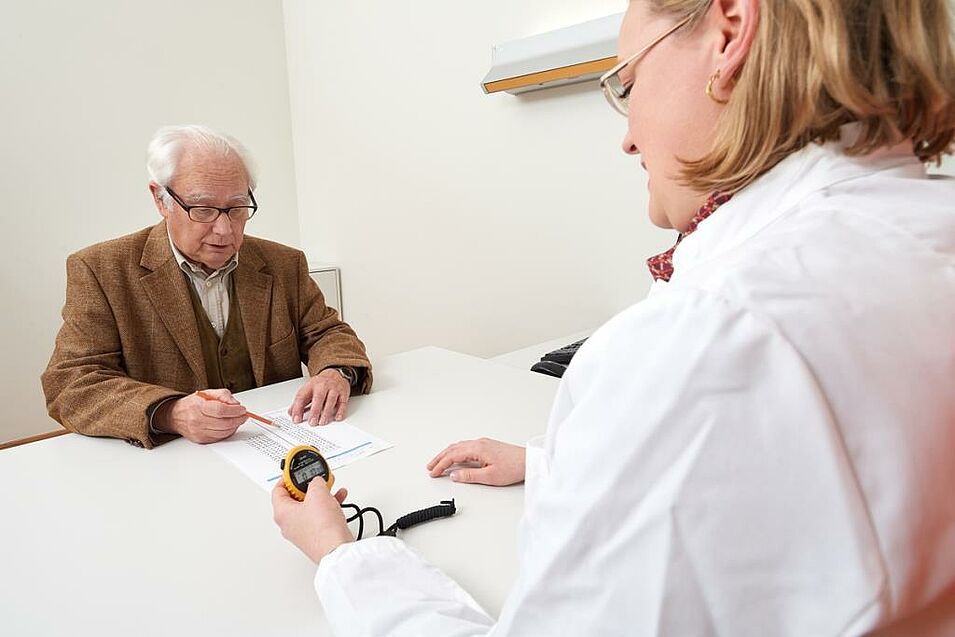
Neuropsychological Assessment
The aim of a neuropsychological assessment is to identify potential limitations of mental functions. For this purpose, special standardized tests are used. In addition, self-reports by probands, third-party reports by relatives and behavioral observations are also included. This enables various aspects of performance such as perception, attention, memory and speech, but also emotional experience, personality and everyday behaviour to be recorded and assessed with regard to possible disease-related changes.
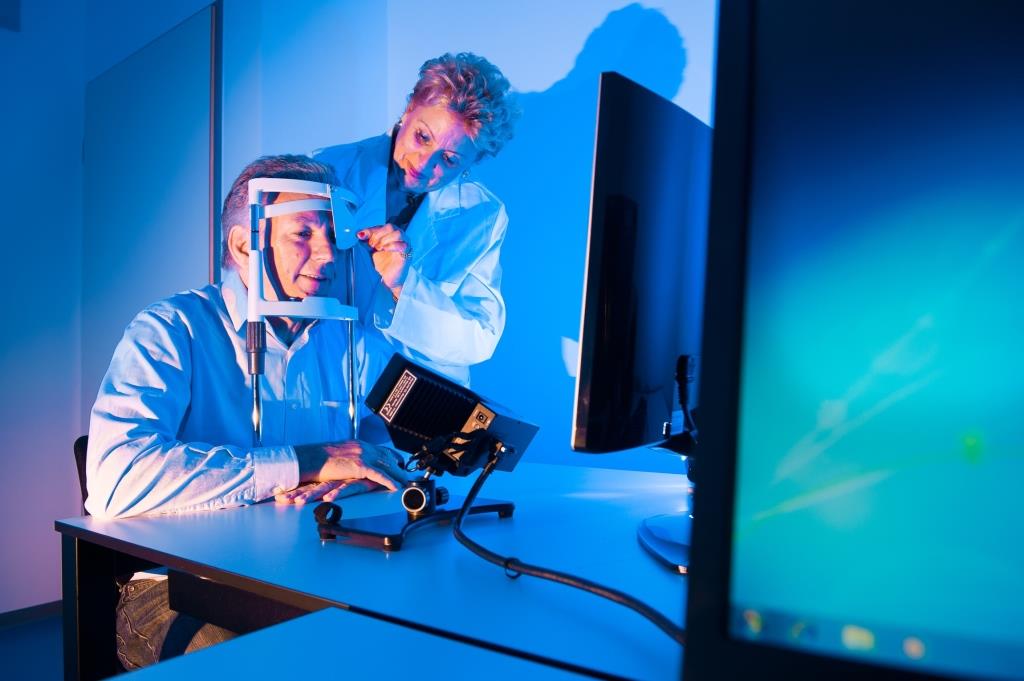



Oculography - Recording of eye movements (eye tracking)
The use of an eye tracker in clinical studies makes it possible to investigate the relationship between eye movement disorders and cognitive and motor changes in the context of neurodegenerative diseases.
The eye movement is recorded by a camera using a weak infrared light beam and is neither unpleasant nor harmful to the eyes.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) allows an exact representation of the ocular fundus (including papilla, macula and choroid). With the help of harmless laser light, an image-layer image of the retina can be taken in a short time without exposure to radiation or contact with the eye.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
PET is a nuclear medicine method that allows insights into various aspects of brain function, including brain glucose metabolism, depositions of disease-related proteins (e.g. beta-amyloid), or the availability of receptors for brain transmitters (e.g. dopamine).
This procedure is done in cooperation with the Clinic and Polyclinic for Nuclear Medicine of the University Hospital Bonn.
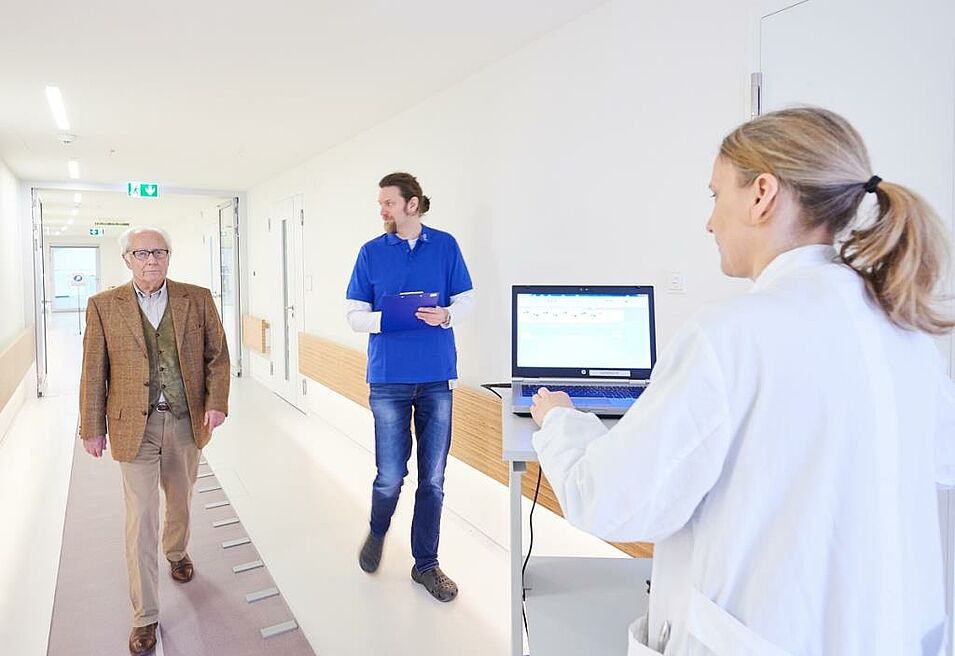
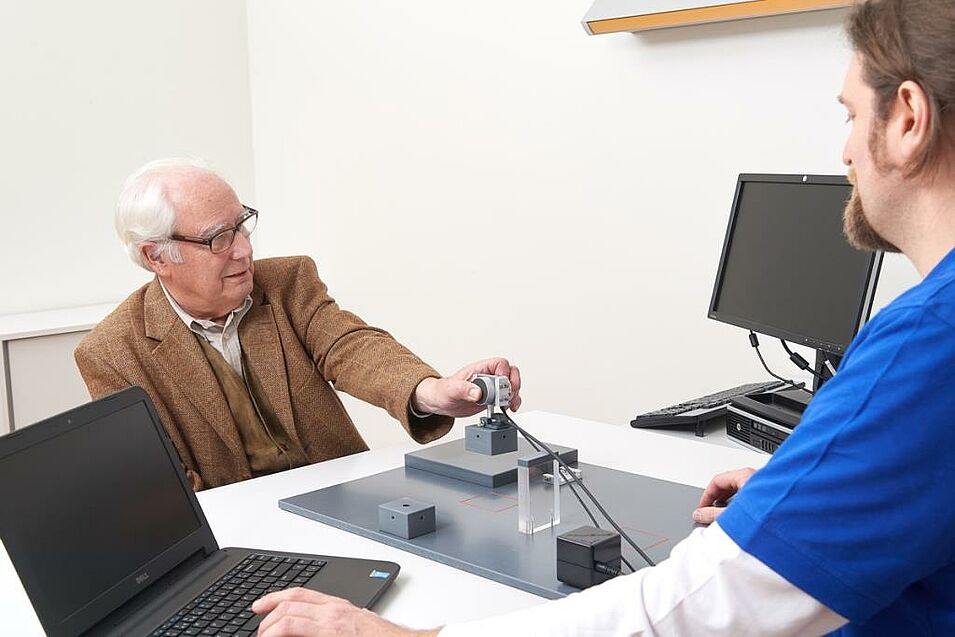
Quantitative motor methods / actigraphy / gait analysis
By means of special equipment, motor anomalies e.g. gait disturbances can be objectively measured. The use of these quantitative techniques makes it possible to detect disorders much earlier and to objectively identify the effects of new therapies.



Spiroergometry
Spiroergometry is used in our studies on the influence of physical training on cognitive functions and the volume of certain brain areas.
The subject sits on a special bicycle (ergometer), the load (watt) is increased by 10-50 watts in 2-minute intervals. During this exercise, the ECG and blood pressure are controlled, the respiratory gases (oxygen intake/consumption) are measured via a mask on the mouth and nose.
Spiroergometry reflects the interplay of heart, lung, circulation and metabolism and is used in sports medicine/performance diagnostics. It can be used as an objective measure of training success.
Ultrasound examination (Sonography)
This is a side-effect-free imaging examination without radiation exposure, which can be used to visualize changes in the vascular walls (e. g. brain-supplying vessels in the cervical region or in the head), changes in brain tissue (e. g. changes in the signaling behaviour of the substantia nigra in Parkinson's disease) and changes in peripheral nerves.
